narrowband IoT (NB-IoT)
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) is a wireless internet of things (IoT) protocol using low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technology. It was developed by 3GPP for cellular wireless communication that enables a wide range of new NB-IoT devices and services. NB-IoT is one of the three main 3GPP LPWAN standards.
The NB-IoT communication standard is aimed at enabling IoT devices to operate via carrier networks, either within an existing Global System for Mobile (GSM) communication carrier wave, in an unused “guard band” between LTE channels or independently.
One of the goals of NB-IoT is to boost the coverage extension beyond what existing cellular technologies offer. To do that, NB-IoT offers transmission repetitions and different bandwidth allocation configurations in uplink transmission.
NB-IoT can enable a broad range of new IoT devices and services. NB-IoT reduces the power consumption of connected devices, while increasing system capacity and bandwidth efficiency, particularly in locations that aren’t easily covered by traditional cellular technologies. NB-IoT connected devices can have a battery life of more than 10 years for many use cases.
To date, 159 operators have invested in NB-IoT with 107 deployed/launched networks worldwide.
How does NB-IoT work?
NB-IoT is a data transmission standard designed to enable devices to operate in mobile carrier networks. NB-IoT technology uses low bandwidth signals to communicate within existing GSM and LTE technologies.
Specially designed devices and sensors are the basic components in NB-IoT systems. These devices collect information from their surroundings and transmit it to NB-IoT base stations or transmission nodes. Individual base stations are connected to an IoT gateway and IoT cloud application servers for centralized monitoring and data analysis.
NB-IoT employs a new physical layer with signals and channels to meet the requirements of extended coverage in rural areas and deep indoors, while enabling very low device complexity. The underlying technology is much less complex than that of GSM/GPRS modules.
Supported by all major mobile equipment, chipset and module manufacturers, NB-IoT can exist along with 2G, 3G and 4G mobile networks.
What are the benefits of NB-IoT?
The benefits of NB-IoT include:
- Ubiquitous coverage and connectivity. NB-IoT can help support massive numbers of devices by establishing NB-IoT networks that can connect to billions of nodes. Designed for extended coverage indoors, the lower complexity of the devices provides long-range connectivity and communication.
- Low power consumption. NB-IoT doesn’t need to run a heavy operating system, such as Linux, or do a lot of signal processing, which makes it more power efficient compared to other cellular technologies.
- Low cost of devices. Because it’s easier to create devices with lower complexity, the cost of the devices is significantly low, around $5 per module.
- Multiyear battery life. The enhanced power consumption capability enables NB-IoT to support a multiyear battery life for devices.
- Security. NB-IoT is secured much like 4G, including all encryption and SIM-based authentication features.
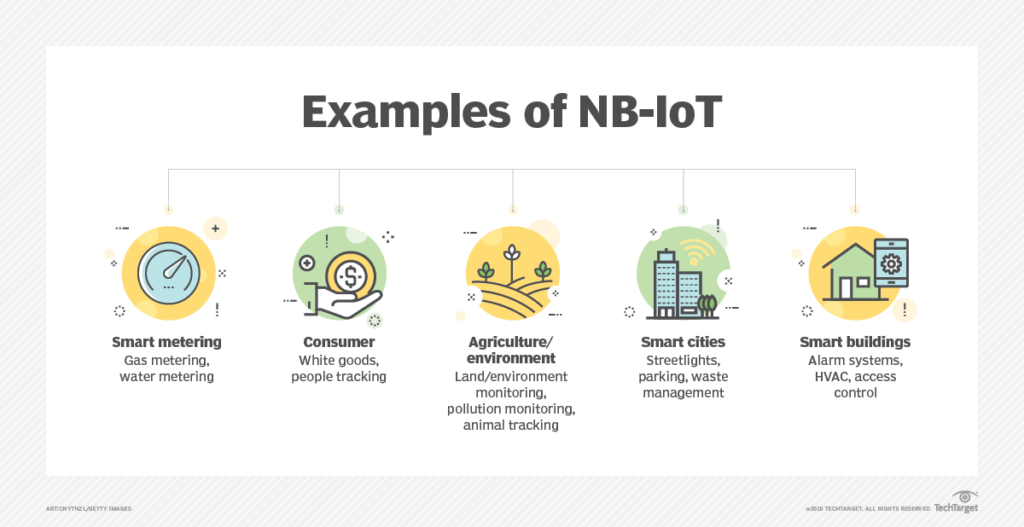
Examples of NB-IoT applications
NB-IoT can be used for the following applications:
- Smart metering. NB‑IoT works well for monitoring water and gas meters via regular and small data transmissions. Network coverage is a major problem in rolling out smart metering as meters are often installed in difficult locations, such as deep underground, in cellars or in remote rural areas. NB‑IoT coverage and penetration are able to address this issue.
- Smart cities. NB‑IoT can help local governments control street lighting, determine when trash bins must be emptied, identify free parking spaces, monitor environmental conditions and survey road conditions.
- Smart buildings. NB‑IoT connected sensors can send alerts to facilities managers regarding building maintenance issues. There are also indoor temperature monitoring systems that are based on NB-IoT sensors. NB‑IoT can serve to back up a building’s broadband connection.
- Tracking. NB‑IoT provides a secure, inexpensive way to track people, animals and assets when continuous tracking isn’t necessary. NB-IoT is good for tracking objects that may not be moving all the time.
- Smart farming. NB‑IoT connectivity enables farmers and cities to capture data from environmental sensors containing NB‑IoT modules that can send alerts if anything out of the ordinary happens. These sensors could be used to monitor the temperature and humidity of the soil, as well as to track the attributes of land, pollution, noise and rain.